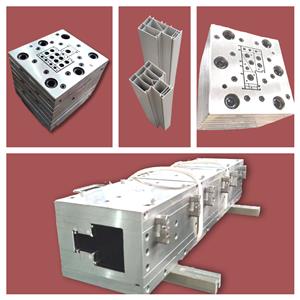
PVC-Kunststoff, die Konstruktion der Extrusionsform, enthüllt den Schleier für Sie
Es werden üblicherweise zwei Formen von Formen verwendet: Platten-Stufen-Formen und Querschnitt-Gradienten-Formen. Der Fließweg der Plattenstufenform verändert sich stufenweise, die aus mehreren hintereinander geschalteten Mündungsschablonen besteht. Jede Platte wird in eine entsprechende Konturform bearbeitet, die sich allmählich von der runden Form des Einlasses zur gewünschten Auslassform ändert. Am Eingang jedes Blocks befinden sich Abschrägungen, um den Übergang von einer Form zur anderen zu vervollständigen. Die Verarbeitungskosten dieser Form sind gering, der Strömungskanal ist nicht ideal stromlinienförmig und muss im Allgemeinen nicht als Hauptprofil verwendet werden. Der Formkanal mit Abschnittsgradient ist stromlinienförmig, es darf keine Rückhaltezone des Materials im Kanal vorhanden sein, die Schmelze wird vom Kreis am Einlass allmählich und genau auf jeden Abschnitt der Auslassform verteilt und die Geschwindigkeit wird stetig erhöht erforderliche Auslassgeschwindigkeit, und die Geschwindigkeit jedes Punktes auf dem Abschnitt ist gleich. Bei PVC-Kunststoffprofilen mit komplexen Formkernen ist der Formkern entweder in die Halterungsplatte integriert, einige werden durch Positionierungsstifte und Schrauben an der Halterungsplatte befestigt, andere werden durch feste Einlage in die Halterungsplatte eingebettet. Es kann während des Gebrauchs nicht einfach zerlegt werden, da es zeitaufwändig ist, es wieder zusammenzubauen und zu debuggen. Die Umleitung der Schmelze erfolgt ebenfalls auf zwei Arten: am Umleitungskegel und im Kompressionsteil. Die Abschnittsverlaufsform kann als Hauptprofilform verwendet werden. Die Extrusionsform für PVC-Kunststoffprofile ist der Kernbestandteil der Extrusionsproduktionslinie, zu der die Munddüse (auch als Düsenkopf bekannt), die Formgebung, der Kühlwassertank usw. gehören. Die Munddüse wird mithilfe von Mitteln mit dem Flansch am Extruderkopf zusammengebaut eines Flansches, und der Heizring, die Heizplatte, die Stromversorgung und das Thermoelement werden angeschlossen. Die Formform und der Kühlwassertank werden mit Schrauben am Formtisch befestigt und die Wasserleitung und die Gasleitung angeschlossen. Die Grundstruktur der Extrusionsdüse besteht im Allgemeinen aus einer Struktur aus mehreren gestapelten und zusammengesetzten Schablonen. Daher wird der Strömungskanal der gesamten Matrize durch die Verbindung eines der Strömungskanäle in jedem Teil der Schablone, Vorder- und Rückseite, gebildet. Die Platte wird positioniert und mit Stiften und Bolzen befestigt, um eine monolithische Extrusionsdüse zu bilden. Die Grundsituation ist: Der stetige Strömungsabschnitt der Extrusionsdüse besteht häufig aus einer Lochplatte und der vorderen Halshälfte, und die vordere Hälfte und die zweite Halshälfte sind ebenfalls als zwei Schablonen gestaltet, der Hals und der Halsübergangsplatte. Es ist auch möglich, keine poröse Platte zu verwenden, sondern die vordere Hälfte des Halsströmungskanals als zylindrischen Strömungskanal zu gestalten, um die Strömung zu stabilisieren. Der geteilte Abschnitt der Extrusionsdüse beginnt in der zweiten Halshälfte und umfasst den geteilten Konus, die geteilte Halterungsplatte und die Schrumpfplatte. Die Schrumpfplatte kann nicht in eine einzelne Schalung, sondern zusammen mit der vorgeformten Platte – einer Schalung – geteilt werden. Der Formungsabschnitt der Extrusionsdüse umfasst die folgenden Schablonen: Hohlraumplatte (auch als vorgeformte Platte bekannt), Mündungsschablone (auch als Formplatte bekannt) und Kern (auch als Formkern bekannt). Bei einfacheren Profilformen wird die vorgeformte Platte mit der Mundschablone zu einer Schalung zusammengefasst. 1. Kernpunkte des Produktquerschnittdesigns Der Kernpunkt des Produktdesigns von PVC-Kunststoffprofilen besteht darin, dass die Dicke und Form jedes Abschnitts symmetrisch verteilt sein sollte, damit der Materialfluss im Maschinenkopf ausgeglichen ist und die Kühlung gleichmäßig erfolgen kann , und der Druck ist tendenziell ausgeglichen. Im Allgemeinen sind die maximale Wandstärke und die minimale Wandstärke desselben Abschnitts unterschiedlich < 50% is appropriate. If it is a part of a closed rib, the thickness of the rib should be 20% thinner than the wall thickness. In order to avoid the stress concentration at the corner of PVC plastic profile products, the shape change of the product should be smooth and smooth transition, generally the outer corner R is not less than 0.5mm, the inner corner R is not less than 0.25mm. The hollow part of the product should not be too small. The cross-sectional shape is preferably symmetrical. 2. Structure type and design principle of mold The mold is the forming part of the extruder, which is mainly composed of neck seat, shunt cone, support plate (also known as bracket), core mold, mouth template and adjusting screw. PVC plastic profile extrusion die county is mainly composed of three sections: feeding section one by machine base and distribution cone composed of machine head flow channel feeding section, is conical: melt distribution and forming section one by support plate and mouth die compression part constitute melt distribution and forming section, the shape is gradually close to the PVC plastic profile section, parallel section mouth die and core die constitute the machine head parallel section, (1) There are two types of mold structure for extruded plastic profiles: plate head and streamlined head. According to the different methods of processing and manufacturing the machine head, the streamlined head fork is divided into integral streamlined and segmented (also known as stepped) streamlined. (2) Mold design principle The mold is the key part of PVC plastic profile extrusion, and its function is to extrude a blank similar to the profile under the action of 10~25MPa extrusion force. PVC plastic profile mold runner design principle is that the runner section should be streamlined: there is enough compression ratio and shaped length to form a certain extrusion pressure: the flow resistance balance and flow symmetry of the cross-sectional gap of each runner part of the mold. The flow channel structure of the PVC plastic profile head is generally divided into three parts: feeding, compression (also known as transition part) and forming. Generally speaking, the length of the feed part of the long runner is 1 of the length of the shaping part. About 5~2 times, the length of the compression part is about 2~3 times the length of the shaping part. The maximum cross-sectional area of the compression section is in the outlet area of the bracket. The shape of the support ribs of the bracketer. The broad one is jujube nucleus-shaped. The thin ones are long prismatic. The shape of the divergence in the front of the scaffold is that it converges at the same angle on all sides, forming a torpedo body shape. The flow rate of molten material is different in the flow channel of feeding, compression and forming, the feeding part is the smallest, the forming part is the largest, and the transition part must be in between the two and gradually increase in the direction of extrusion. The melt flow rate is inversely proportional to the cross-sectional area of the runner. The roughness of the runner in the head should be Ra0. 4~0.8ym, the roughness of the mouth mold runner of the stereotyped part is higher than the roughness of the inner runner, which should be Ra0.2~0. 4μm, When the extruded billet is just exported to the die, the size of the gap is increased than the mouth die, which is called the mold release expansion, that is, the Balas effect. This effect must be considered when the pulling speed of PVC plastic profile extrusion is slow and it is cooled near the outlet of the die mold. The release mold expansion of the outlet die is usually calculated by volume, and its expansion rate is generally 1.5~2.5 times, and this value changes with different aspects of melt temperature, pressure and velocity. The wall thickness size required for PVC plastic profiles depends on the wall thickness of the appropriate extruded billet on the one hand, and the pulling speed and extrusion amount on the other hand. The thickness of the extrusion blank wall mainly depends on the size of the mouth die gap, and then depends on the plasticizing performance of the material in the extruder, extrusion pressure, extrusion temperature, material performance and expansion value. First, the standard traction shrinkage rate for general wall thickness is ≤2.5%. The gap between the mouth die and the thickness of the product are taken (0.8~0.9) 1 1